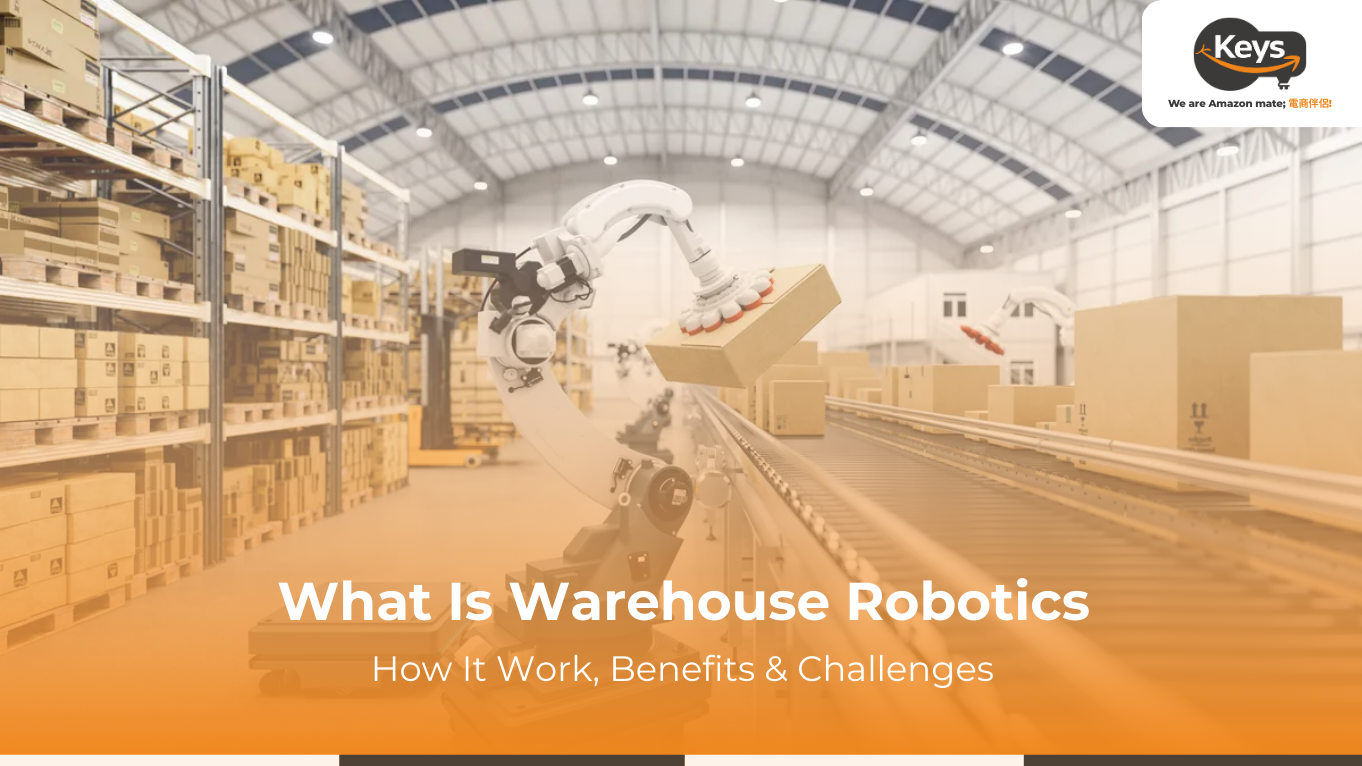
Warehouse robotics is transforming the logistics industry by automating repetitive tasks, improving accuracy, and increasing overall operational efficiency. From autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) that transport goods across the warehouse to robotic arms that handle picking and packing, these technologies enable warehouses to meet growing e-commerce demand and seasonal peaks. By integrating robotics with warehouse management systems, businesses can optimize workflows, reduce errors, and enhance real-time inventory visibility. As companies strive for faster delivery, lower costs, and higher customer satisfaction, warehouse robotics has become a critical component of modern supply chain strategies.
What Is Warehouse Robotics?
Warehouse robotics refers to the use of automated machines, robots, and intelligent systems to assist with storage, retrieval, picking, packing, and shipping within warehouse operations. These robotic solutions are designed to increase efficiency, reduce labor costs, and improve accuracy in handling goods. Unlike traditional warehouse methods that rely heavily on human labor, warehouse robotics integrates technology to streamline processes and reduce manual intervention.
Modern warehouses face ever-increasing demand for faster delivery, higher accuracy, and flexible operations. Robotics helps achieve these goals by automating repetitive tasks and allowing human workers to focus on more complex, value-added activities. From autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) that transport inventory to robotic arms that pick and pack products, warehouse robotics encompasses a wide variety of solutions that cater to different operational needs.
By combining robotics with warehouse management systems (WMS) and artificial intelligence (AI), warehouses can operate around the clock, optimize inventory flows, and meet customer expectations more efficiently. In an era of rapid e-commerce growth, warehouse robotics is becoming a critical part of supply chain modernization.

Types of Warehouse Robotics
Warehouse robotics can be classified based on functionality, mobility, and the tasks they perform. Key types include:
Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs)
AMRs are self-navigating robots that transport inventory across the warehouse floor. Unlike traditional automated guided vehicles (AGVs), AMRs use sensors, cameras, and AI algorithms to detect obstacles and plan optimal paths. They can move pallets, bins, or cartons efficiently without the need for predefined tracks, improving warehouse flexibility.
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs)
AGVs follow fixed paths using magnetic strips, wires, or markers on the warehouse floor. They are primarily used to transport heavy loads over long distances within large facilities. AGVs are highly reliable but less flexible than AMRs due to their reliance on predetermined routes.
Robotic Picking Arms
Robotic arms are designed to pick and place products, often integrated with vision systems for object recognition. They can handle items of various shapes, sizes, and weights. Advanced picking robots can work alongside humans or fully autonomously to streamline order fulfillment.
Collaborative Robots (Cobots)
Cobots work safely alongside human workers, assisting with tasks like picking, packing, and palletizing. They are equipped with sensors to detect human presence and can be programmed for repetitive operations, enhancing productivity without replacing the workforce entirely.
Sorting and Packing Robots
These robots automate the process of sorting items based on size, weight, or destination. Packing robots can place products into boxes, label them, and prepare them for shipping. They help reduce errors and increase throughput, especially during peak seasons.
Inventory Scanning Robots
Equipped with cameras and RFID readers, these robots continuously monitor inventory levels, scan barcodes, and update warehouse management systems in real-time. They improve accuracy, reduce stock discrepancies, and assist with cycle counting.
Palletizing and Depalletizing Robots
These specialized robots handle heavy pallets, stacking and unstacking products efficiently. They are particularly valuable for warehouses dealing with bulk goods or industrial products, reducing labor strain and minimizing workplace injuries.
Benefits of Warehouse Robotics
Implementing robotics in warehouses provides transformative advantages that go beyond simple automation:
Increased Productivity
Robots can work continuously, 24/7, without fatigue, significantly outperforming human labor in repetitive tasks. For example, autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) can transport hundreds of units across a warehouse per hour, enabling higher throughput during peak seasons. By offloading repetitive tasks, human workers can focus on complex or quality-sensitive operations, further boosting overall productivity.
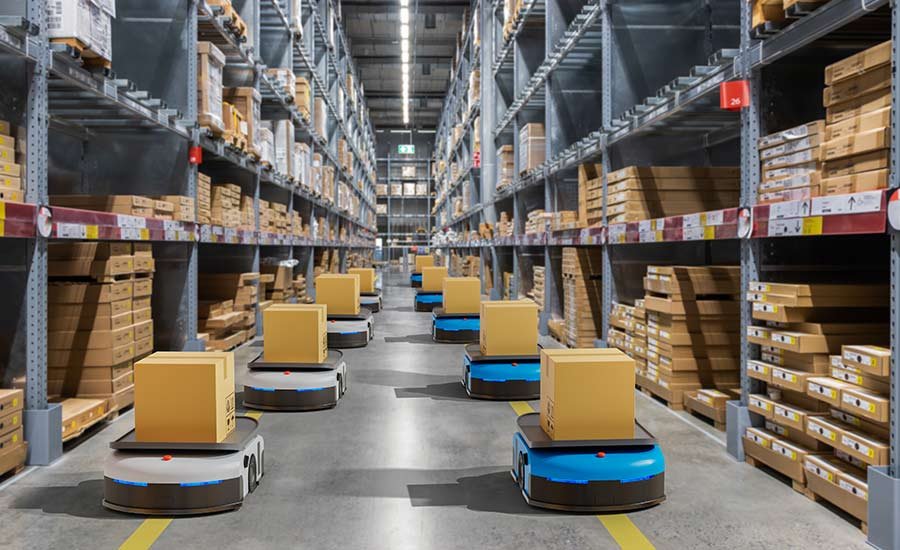

Improved Accuracy
Picking errors, misplaced inventory, or incorrect packing can be costly. Robotic arms equipped with advanced vision systems and AI algorithms reduce errors dramatically. For instance, order accuracy in robotic-assisted warehouses can exceed 99.9%, minimizing returns and increasing customer satisfaction.
Cost Savings
While initial investment in robotics is high, long-term operational costs are significantly reduced. Labor costs are minimized, overtime expenses during peak periods decrease, and efficiency gains reduce waste. Over time, the return on investment (ROI) from reduced errors, faster order processing, and optimized storage often outweighs upfront costs.
Enhanced Safety
Robotics takes on heavy lifting, repetitive tasks, and handling hazardous materials. This reduces workplace injuries and creates a safer environment. Palletizing robots, for example, can handle loads exceeding 50 kilograms, minimizing strain-related injuries among staff.
Scalability
Warehouse robotics allows businesses to scale operations quickly without hiring additional temporary workers during peak periods. This flexibility is essential for e-commerce fulfillment, especially during holiday seasons or flash sales.
Optimized Space Utilization
Automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS) enable vertical storage, dense packing, and more efficient aisle layout. For instance, goods-to-person systems reduce aisle space by moving inventory to the worker, freeing up valuable square footage.
Real-time Inventory Visibility
Robots integrated with warehouse management systems (WMS) provide continuous inventory updates. Automated scanning of items ensures accurate stock levels, supports just-in-time replenishment, and improves demand forecasting.
Enhanced Customer Experience
Faster processing, higher accuracy, and shorter lead times directly improve customer satisfaction. Timely deliveries, fewer errors, and consistent service quality enhance brand loyalty.
Challenges of Warehouse Robotics
Despite its benefits, implementing robotics comes with challenges:
High Initial Investment
Purchasing robots, sensors, software, and infrastructure upgrades can be costly, especially for small and mid-sized enterprises. ROI may take several years, requiring careful financial planning.
Complexity of Integration
Seamless integration with WMS, ERP systems, conveyor belts, and human workflows is crucial. Poor integration can lead to workflow disruptions, errors, or downtime.
Maintenance and Downtime
Robots require regular maintenance and software updates. Unexpected downtime can halt operations if backup plans or manual processes are not in place. Predictive maintenance can mitigate these risks but requires additional investment.
Workforce Adaptation
Employees may need retraining to work alongside robots or operate robotic systems. Resistance to change can initially slow productivity. Clear communication, hands-on training, and role redefinition help overcome this challenge.
Limited Flexibility for Certain Tasks
Robots excel in repetitive, structured, or predictable tasks but struggle with irregular, delicate, or custom-handled items. Advanced AI and vision systems are improving this limitation, but human oversight is still necessary for many applications.
Cybersecurity Concerns
Connected robotics rely on networks and cloud systems, making them potential targets for cyberattacks. Breaches can disrupt operations or compromise sensitive inventory data. Implementing strong cybersecurity protocols is essential.

How Warehouse Robotics Works
Warehouse robotics integrates hardware, software, and intelligent systems to streamline operations. Key steps include:
- Task Assignment: The WMS assigns tasks to robots based on priorities, location, and workload. This could include picking, transporting, packing, or sorting orders.
- Navigation & Movement: AMRs or AGVs navigate warehouse floors using sensors, cameras, or pre-defined tracks. AI algorithms help avoid obstacles and optimize travel routes.
- Item Identification: Robots utilize vision systems, RFID readers, or barcode scanners to locate, identify, and verify items accurately.
- Execution: Robots carry out assigned tasks autonomously, while collaborative robots (cobots) assist humans in tasks requiring flexibility.
- Feedback & Updates: Task completion is confirmed automatically, and inventory levels are updated in real-time within the WMS.
- Optimization: AI-powered algorithms continuously improve routing, task assignment, and workflow efficiency, minimizing downtime and maximizing output.
Implementing Warehouse Robotics
A structured approach ensures successful implementation:
Assess Warehouse Needs
Evaluate which processes (picking, packing, storage, or transportation) will benefit most from automation.
Select Appropriate Robotics
Choose robots tailored to warehouse layout, product types, and operational goals. AMRs are ideal for material movement, robotic arms for picking, and cobots for collaborative tasks.
Integrate with WMS
Ensure robots are fully connected with the warehouse management system to track inventory, assign tasks, and monitor performance.
Train Workforce
Employees must learn to operate, monitor, and maintain robotic systems and adapt to new processes.
Pilot Testing
Deploy a small-scale trial to evaluate performance, identify challenges, and optimize workflows before full-scale implementation.
Monitor and Optimize
Continuously analyze metrics such as throughput, accuracy, downtime, and robot utilization. Data-driven adjustments optimize warehouse efficiency.

Improving Efficiency with Warehouse Robotics
Warehouse robotics enhances operational efficiency in numerous ways:
Automated Picking and Packing
Robots handle repetitive picking and packing tasks quickly and accurately, reducing labor costs and minimizing human errors.
Real-time Inventory Management
Robots continuously scan and track inventory, providing accurate, real-time data for replenishment and demand planning.
Faster Order Processing
Automation shortens order cycle times, allowing warehouses to meet same-day or next-day shipping requirements.
Space Optimization
AS/RS and goods-to-person systems improve storage density, maximizing warehouse capacity without increasing footprint.
Integration with Supply Chain Systems
Robotics can interface with TMS and ERP systems, streamlining end-to-end logistics from supplier to customer.
Flexibility for Seasonal Peaks
During high-demand periods, robotics handles increased order volumes without hiring additional staff, maintaining consistent throughput.
Predictive Maintenance
Robots can signal maintenance needs before breakdowns occur, reducing downtime and ensuring uninterrupted operations.
Data-Driven Decision Making
By collecting detailed operational data, warehouse managers can make informed decisions to optimize layout, workflows, and resource allocation.
Warehouse robotics is no longer a futuristic concept-it is a practical solution for businesses seeking efficiency, accuracy, and scalability in their operations. By automating repetitive tasks, optimizing storage, and providing real-time inventory visibility, robotics enables warehouses to meet increasing customer demands while reducing costs and errors. Despite challenges such as high initial investment and integration complexity, careful planning, workforce training, and the right technology can unlock significant long-term benefits. As the logistics industry continues to evolve, adopting warehouse robotics will be key for companies aiming to stay competitive, agile, and future-ready.











 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt 中文 (中国)
中文 (中国)

