For small businesses navigating growth and expansion, finding the right warehousing solution is crucial. A reliable warehousing system ensures both inventory management and customer satisfaction. This guide will explore the best warehousing solutions tailored for small businesses, then provide a practical roadmap to selecting the one that aligns perfectly with operational needs and budget constraints.
Definition of small business warehousing
Small business warehousing refers to the storage solutions and operational processes that cater specifically to the needs of small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) within the logistics sector. Small business warehousing typically involves more flexible, cost-effective, and scalable storage facilities. These warehouses can range from shared spaces within a larger third-party logistics (3PL) facility to dedicated, or smaller buildings designed to accommodate limited inventory volumes.

Why warehousing matters for SMBs
Here are several reasons why warehousing matters for SMBs:
- Inventory management: Warehousing enables small to medium-sized businesses (SMBs) to manage stock levels effectively, reducing the risk of stockouts and overstocking, which can tie up capital and increase costs.
- Order fulfillment: A well-organized warehouse enables faster and more accurate order processing, ensuring customers receive their products on time and in good condition.
- Scalability: As SMBs grow, warehousing solutions can scale to accommodate increased inventory, seasonal fluctuations, and expanded product lines.
- Supply chain efficiency: Centralized warehousing helps streamline logistics by consolidating shipments, optimizing transportation routes, and reducing lead times.
- Cost optimization: By using shared warehousing or third-party logistics providers (3PLs), SMBs can reduce overhead costs compared to investing in their own facilities.
- Improved customer experience: Timely and accurate deliveries from an efficient warehouse operation enhance customer satisfaction and build brand loyalty.
- Risk mitigation: Warehousing provides a buffer against supply chain disruptions, such as supplier delays or unexpected spikes in demand.

When & why your small business needs warehousing
Future proofing
Warehousing provides SMBs with the flexibility to scale their operations in response to changing market demands. By securing dedicated storage space, businesses can prepare for fluctuations in product volume, seasonal peaks, and unexpected supply chain disruptions. From that, SMBs remain agile and competitive in a dynamic logistics landscape.
Ensuring visibility
Warehousing solutions equipped with modern inventory management systems enable SMBs to track stock levels in real-time. Visibility across the entire supply chain fosters informed decision-making, accurate forecasting, and faster response to demand changes. This minimizes stockouts and overstocking, enhancing customer satisfaction.

Shipping
Efficient warehousing supports optimized shipping processes, including order picking, packing, and last-mile delivery. By strategically locating warehouses near key markets, small to medium-sized businesses (SMBs) can reduce transit times and shipping costs, thereby improving service levels and enhancing customer experiences.
Managing inventories
Proper inventory management within a warehouse enables small to medium-sized businesses (SMBs) to maintain accurate stock records, track product movement, and implement just-in-time replenishment strategies. This reduces excess inventory, lowers carrying costs, and frees up working capital that can be reinvested into business growth.

Enhanced production processes, improved quality, optimized storage, and more
A well-managed warehouse enhances production efficiency by streamlining the storage and handling of raw materials and finished goods. This leads to better quality control, reduced product damage, and efficient order fulfillment. In turn, businesses can meet customer expectations while maintaining consistent product standards.
Types of Warehousing Solutions
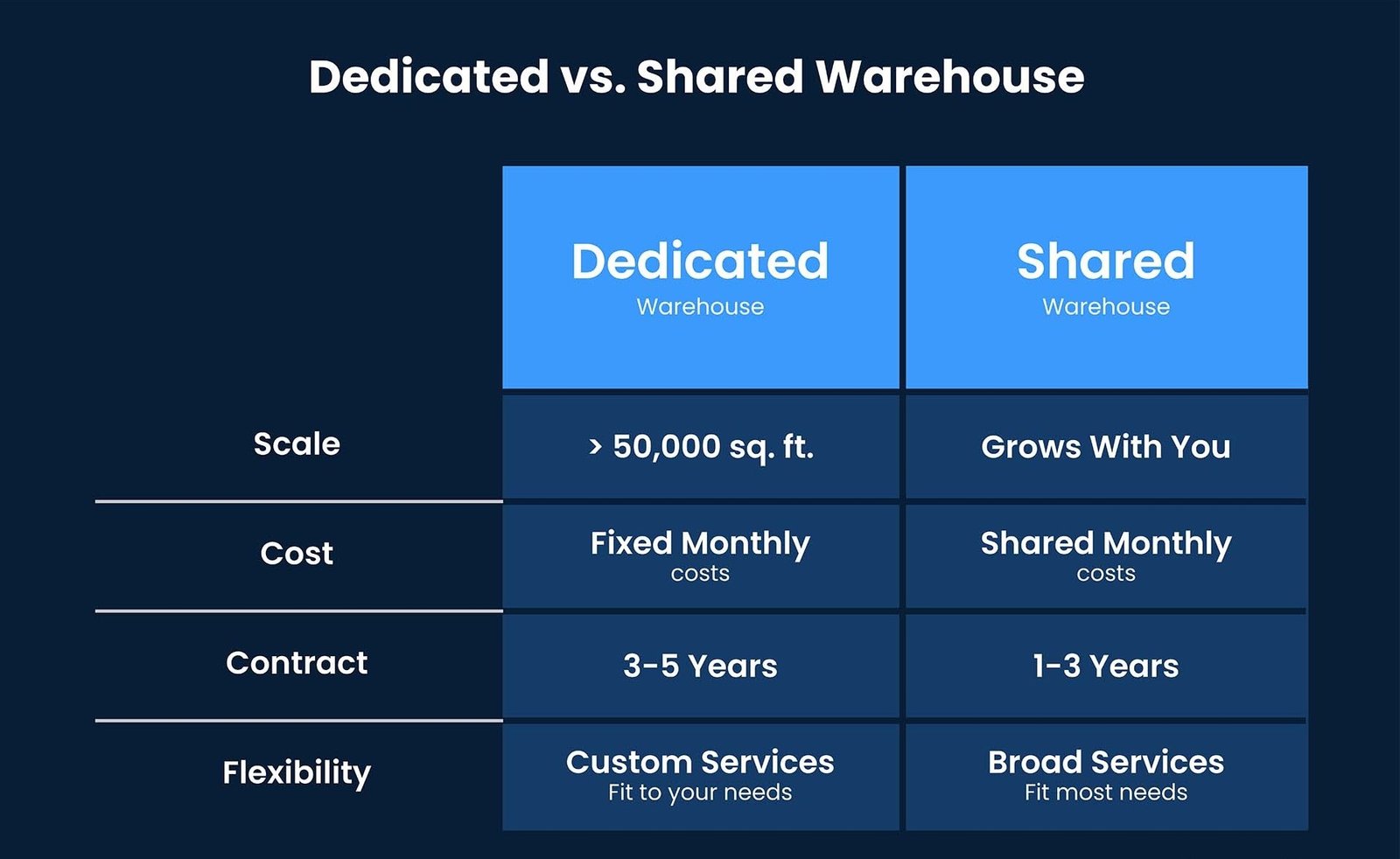
Dedicated Warehouses vs. Shared (Co-warehousing)
Dedicated warehouses provide logistics companies with full control over their storage space, offering consistent capacity, tailored layouts, and customized handling processes. This solution is ideal for businesses with high-volume, consistent inventory turnover or those requiring specialized equipment, such as cold storage or hazardous materials handling. A dedicated warehouse arrangement also allows for branding consistency, as companies can control the environment and operational protocols.
In contrast, shared warehousing (co-warehousing) enables multiple businesses to share a single facility, optimizing space utilization and reducing fixed costs. This flexible model is particularly advantageous for small to medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) or seasonal businesses with fluctuating inventory levels. Shared warehousing allows companies to pay only for the space and services they use, such as pick-and-pack or cross-docking, while also benefiting from economies of scale.
On-Demand/Pop-Up Warehousing
On-demand or pop-up warehousing caters to businesses that need short-term or flexible storage solutions. This model supports scalability during peak seasons, product launches, or unexpected demand surges.
Pop-up warehousing is particularly effective for e-commerce retailers seeking to position inventory closer to key markets. These facilities often integrate with cloud-based warehouse management systems (WMS) that enable real-time inventory tracking and seamless integration with existing supply chains.
Third-Party Logistics (3PL) Providers
Third-party logistics (3PL) providers offer comprehensive warehousing solutions that encompass inventory management, order fulfillment, and value-added services such as kitting, labeling, and reverse logistics. By outsourcing these functions to a 3PL, businesses can focus on their core competencies while benefiting from the provider’s infrastructure and expertise.

Bonded Warehouses & Foreign-Trade Zones
Bonded warehouses and foreign-trade zones offer specialized solutions for companies involved in international trade. A bonded warehouse is a secure facility of customs authorities where imported goods can be stored without the immediate payment of duties and taxes. This allows businesses to defer payments for customs duties or taxes until the goods enter the domestic market.
Foreign-trade zones extend these benefits by providing duty exemptions, deferrals, and even reductions for goods that are re-exported or transformed through manufacturing or assembly processes. Foreign-trade zones are particularly advantageous for industries like automotive, electronics, and pharmaceuticals, where component assembly and global sourcing are integral to operations.
What type of warehouse do you need?
Below, key considerations are outlined to help businesses make informed decisions about this essential choice:
- Selecting the Right Warehouse Partner: A reliable warehouse partner should have a proven track record of handling similar product categories, managing seasonal peaks, and supporting omnichannel fulfillment. By aligning with a trusted partner, businesses can mitigate risks and ensure consistent service levels throughout their supply chain.
- Location & Transit Times: Companies should analyze their customer base and supply chain routes to identify the most advantageous warehouse location for their operations. A strategically situated facility near key markets or transportation hubs reduces lead times and shipping costs, enhancing service levels. Proximity to major ports, airports, and intermodal terminals also enables faster replenishment cycles, which is essential for maintaining optimal inventory levels.
- Pricing Models & Minimums: Warehouses may offer different pricing structures, including transactional rates, volume-based discounts, or flat fees. Therefore, businesses should review these terms carefully and assess whether they align with their demand patterns and cash flow projections. Transparent pricing models empower companies to forecast expenses accurately and avoid hidden charges.
- Service Offerings (Kitting, Returns, Value-Added): A warehouse that offers these services can reduce the need for additional partners, simplifying coordination and communication. Companies should identify the specific services that align with their business needs to maximize operational efficiency and brand differentiation.
- Technology Integration (WMS, API, Real-Time Tracking): Investing in a tech-forward warehouse partner ensures agility and competitiveness in today’s dynamic logistics landscape.
In conclusion, small businesses seeking the most effective warehousing solutions should carefully assess their unique operational needs and growth goals. By considering factors such as location, scalability, cost, and technological integration, they can make informed decisions that optimize their supply chain efficiency. Ultimately, choosing the right warehousing solution empowers small businesses to remain competitive and responsive in a rapidly changing market.












 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt 中文 (中国)
中文 (中国)

