Inventory kitting is a strategic method used in warehouse and inventory management to streamline the fulfillment process. It involves grouping individual items into ready-to-ship kits based on customer demand or product requirements. This guide of Key Logistics below explores the fundamentals of kitting, its benefits for operational efficiency, and how businesses can implement it to reduce handling time and improve order accuracy.
What Is Kitting?
Kitting is a logistics and inventory management process where individual items are grouped, packaged, and supplied together as a single unit or “kit.” This method streamlines operations by assembling components needed for a specific task, product, or order in advance, reducing handling time and improving efficiency throughout the supply chain. Kitting is commonly used in industries like e-commerce, electronics, automotive, and healthcare, where accuracy and speed are critical to operational success.
What Is Kitting in Logistics?
In logistics, kitting refers to assembling individual items into a single, ready-to-ship package known as a “kit.” Instead of shipping items separately, kitting enables logistics providers to reduce packaging waste, optimize shipping routes, and lower transportation costs. It’s especially beneficial in e-commerce, subscription boxes, and retail, where multiple SKUs are often ordered together.
For instance, a customer purchasing a laptop, charger and mouse may receive all items in one consolidated package. This not only simplifies inventory tracking and improves warehouse efficiency but also enhances the customer experience by reducing wait times and delivery inconsistencies.
What Is Kitting in a Warehouse?
Kitting in a warehouse refers to the process of collecting and combining multiple individual stock-keeping units (SKUs) into a single, ready-to-ship unit. This process is typically performed in the designated kitting or assembly area of the fulfillment center.
Once assembled, the bundled items are assigned a new SKU to simplify inventory tracking and order fulfillment. Kitting helps streamline logistics operations by reducing the number of individual items that need to be picked and packed, leading to faster processing times and fewer packaging materials.

What Are Kitting Services?
Kitting services are specialized fulfillment operations provided by third-party logistics (3PL) providers. These services allow businesses to outsource the kitting process, which can significantly reduce labor costs, minimize storage requirements, and improve order accuracy. By consolidating multiple items into a single shipment, 3PL providers help clients optimize their packaging, reduce shipping expenses, and enhance the overall customer experience.
What Is Kitting in Manufacturing?
In manufacturing, kitting refers to preparing all the components needed for a specific assembly or production task and delivering them as a single kit to the production line. This reduces downtime, ensures accurate parts usage, and supports lean manufacturing practices.
For instance, an automotive manufacturer may provide a technician with a kit of parts for a specific engine build, which helps eliminate the need to source parts individually during the assembly process.

Inventory Kitting Defined
Inventory kitting refers to grouping, packaging, and managing multiple individual items as a single unit or “kit.” With the aid of warehouse management systems (WMS) or enterprise resource planning (ERP) tools, logistics managers can optimize kit assembly and ensure accuracy in order fulfillment. This flexibility supports dynamic inventory strategies and allows companies to adapt quickly to changing customer needs.
Kitting is especially beneficial for e-commerce, electronics, pharmaceuticals, and custom manufacturing businesses. Online retailers, for instance, use kitting to bundle products into curated packages for promotions or subscription boxes. In manufacturing, component kits can be prepared in advance for production lines, reducing downtime and improving workflow efficiency.

Why Is Kitting Important?
Kitting is a crucial strategy in inventory and warehouse management because it enhances operational efficiency, reduces labor costs, and improves customer satisfaction. By pre-assembling kits or using software to manage virtual kits, companies streamline the picking and packing process, significantly cutting down the time it takes to fulfill complex or multi-item orders. This is especially valuable in high-volume order environments like e-commerce fulfillment centers or third-party logistics (3PL) operations.
From a logistics standpoint, kitting also helps reduce human error, standardize packaging, and improve inventory accuracy. Furthermore, it offers a competitive advantage by enabling businesses to provide tailored product bundles that increase average order value.

Benefits of Kitting
Reducing errors
Kitting significantly minimizes picking and packing errors by pre-assembling components into standardized kits. Rather than retrieving multiple individual items for each order, warehouse staff handle one consolidated SKU, reducing the chance of mispicks. With fewer mistakes, companies experience lower return rates and higher customer satisfaction.
Maximizing warehouse space
By organizing related components into single kits, warehouses can better utilize their storage capacity. Instead of storing and managing numerous separate SKUs, kits occupy a smaller, more organized footprint.
This is especially beneficial in facilities where space optimization is critical to scaling operations. Kitting allows for vertical stacking, palletizing, and improved bin organization, contributing to a more efficient warehouse layout and inventory turnover.

Lowering labor costs
Kitting reduces labor intensity by streamlining the picking process. Workers spend less time locating and retrieving individual parts, as kits are prepared in advance and stored as a single inventory item.
This simplification leads to faster picking times and decreases the number of warehouse personnel required for order fulfillment. Additionally, due to the standardized nature of kitted inventory, training new staff becomes more efficient.
Cutting down on shipping costs
When kitted, products can be packaged more efficiently, often into smaller and lighter parcels. This results in lower dimensional weight charges and optimized freight utilization.
Kitting also consolidates shipping tasks, reducing the need for multiple boxes, labels, and tracking numbers. Businesses save on materials and shipping fees, while customers benefit from more compact deliveries.

Boosting sales revenue
Bundled products often encourage customers to spend more, especially when kits are marketed as convenient, value-added packages. Kitting also enables cross-selling opportunities and simplifies promotions, ultimately enhancing revenue streams.
Speeding up shipping processes
Pre-kitted items are quicker to ship because the picking and assembly steps are already completed in advance. This enables faster order turnaround, which is especially valuable for same-day or next-day shipping models. By reducing fulfillment cycle times, kitting supports high service-level agreements (SLAs) and enhances the overall agility of the supply chain.

How kitting helps in manufacturing
In manufacturing, kitting supports just-in-time (JIT) production models by delivering all necessary components to assembly lines in one consolidated package. This reduces downtime, simplifies inventory management, and ensures consistent production flow. When components are organized and pre-assembled, manufacturers benefit from improved workflow efficiency, fewer material shortages, and easier quality control.
The role of kitting in eCommerce
In the eCommerce sector, kitting improves fulfillment efficiency and enhances the unboxing experience for customers. Subscription boxes, promotional bundles, and gift sets are all examples of kitted offerings that add value. eCommerce businesses can reduce SKU complexity, speed up delivery times, and present products more attractively, which leads to better reviews, repeat purchases, and increased brand loyalty.
Private Kitting
Private kitting is a tailored logistics solution in which a third-party service provider assembles various components (often sourced from multiple suppliers) into a single package under a specific brand. This approach streamlines fulfillment operations and enables businesses to offer a fully branded unboxing experience without managing the complexities of inventory coordination or manual packing in-house.
Private kitting services often include value-added options such as custom packaging, branded inserts, user manuals, and marketing collateral. For instance, an electronics brand may provide a list of required components for a tech starter kit—such as software licenses, adapters, and accessories. The private kitting provider then handles the sourcing, inventory consolidation, and final packaging, shipping the completed kits directly to end-users or retailers, all while maintaining the client’s branding across the supply chain.
How to Manage Kitting
The steps in the kitting process
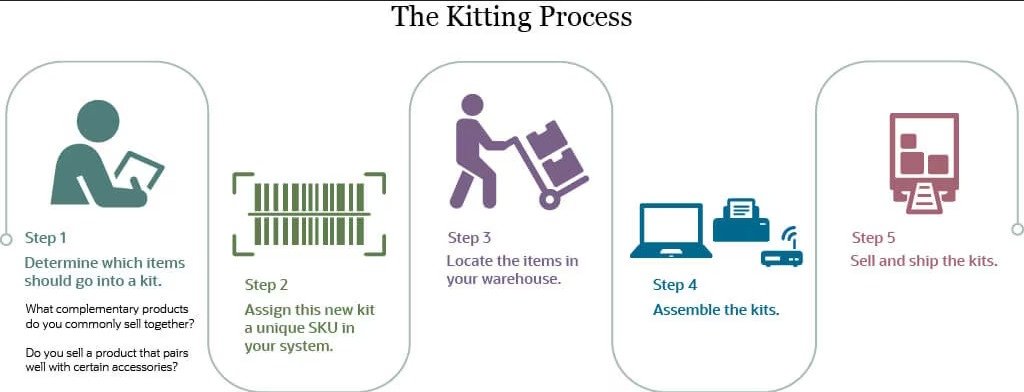
The kitting process involves several structured steps to ensure accuracy and efficiency. Below is a typical sequence followed in logistics operations:
- Identify the kit components: Determine which items should be grouped together based on customer demand or inventory goals.
- Choose who assembles the kits: Decide whether to handle assembly in-house or outsource to a third-party kitting provider.
- Create a unique SKU: Assign a single SKU to the completed kit for simplified inventory tracking and order processing.
- Organize and pack the items: Ensure all components are available, packed safely, and labeled correctly.
- Ship the completed kits: Send the assembled kits to customers or distribution centers, ensuring tracking and documentation are in place.
Identifying the kit components
Determining what items to include in a kit requires a strategic approach based on customer behavior, product lifecycle, and marketing goals. Businesses often analyze sales data to identify products frequently purchased together. For instance, in the logistics or warehousing sector, a company might bundle safety gloves, helmets, and reflective vests into a single “PPE kit” if these items are commonly ordered as a set.
In other cases, companies may use kitting to promote newly launched products by pairing them with bestsellers to boost exposure. Alternatively, slow-moving or surplus inventory can be bundled into kits to accelerate turnover and free up warehouse space. The success of kitting hinges on understanding both operational priorities and customer expectations.

Choosing who assembles the kits
Companies managing kitting operations must decide whether to handle the assembly in-house or contract the task to third-party logistics (3PL) providers. In-house kitting offers more control over quality assurance and flexibility in production schedules, making it ideal for businesses with the necessary labor and storage capacity.
However, outsourcing to a specialized kitting contractor can streamline the supply chain, especially for high-volume or e-commerce fulfillment. These service providers often manage labeling, packaging, and even direct-to-consumer shipping, which can reduce overhead and enhance order accuracy. The choice depends on the company’s logistics capabilities, scalability needs, and cost-efficiency targets.
Creating a unique SKU for each kit
Each kit must be assigned a unique Stock Keeping Unit (SKU) to facilitate accurate inventory tracking, order fulfillment, and reporting. Unlike individual items, kits function as a single product in the warehouse management system (WMS), even though they contain multiple components. A dedicated SKU allows logistics teams to monitor kit availability in real time and prevents errors in picking or restocking.
Furthermore, assigning a unique SKU supports demand forecasting and supply chain optimization. It ensures that every aspect of the kit is traceable, which is critical for both inventory control and customer satisfaction.

Organizing and packing the items
Proper organization and packing are essential to ensure kit integrity and minimize damage during transit. Items should be grouped logically within the packing station, using standardized workflows that optimize speed and accuracy. Warehouses often utilize zone picking or batch picking methods to streamline the process, depending on order volume and product type.
Packing materials should be chosen based on the fragility, size, and shape of the components. Using custom inserts, dividers, or protective wrapping helps reduce the risk of in-transit damage and presents the kit professionally. Clear labeling and kit documentation also support quality control and efficient returns management.
Shipping the completed kits
Once assembled and packed, the completed kits enter the order fulfillment phase, where shipping logistics take center stage. This includes selecting the right carrier, choosing cost-effective shipping methods, and ensuring compliance with service-level agreements (SLAs). For e-commerce orders, fast and accurate shipping is crucial, often requiring integration with real-time tracking systems.
Warehouses may use cross-docking techniques to expedite shipments or rely on a 3PL provider to manage outbound logistics. Regardless of the method, timely delivery and proper handling are essential to maintain customer satisfaction and protect the brand’s reputation in a competitive supply chain environment.
What is a kitting process?
The kitting process in logistics refers to the practice of assembling individual but related items into a single unit, typically before the order is shipped. Instead of picking multiple components separately at the time of order fulfillment, warehouse teams pre-assemble them into kits, which helps reduce lead times and improve operational efficiency. Kitting is commonly used in e-commerce, subscription boxes, electronics, and manufacturing, where components are frequently bundled and shipped together.
From an inventory management perspective, kitting streamlines warehouse workflows by reducing the number of SKUs picked per order. It also helps minimize errors in order fulfillment and allows for better space optimization within the warehouse. By consolidating multiple SKUs into a single packaged unit, logistics teams can simplify stock management, improve accuracy, and enhance the overall customer experience.
How to Implement Kitting with Inventory Management Software
Implementing kitting through inventory management software allows logistics operators to automate the entire process, from tracking individual parts to assembling finished kits ready for shipment.
Modern kitting software generates new SKUs for kits and synchronizes them with the status of the underlying components, providing real-time visibility into stock levels and production capacity. This level of automation reduces human error, speeds up order fulfillment, and ensures better stock rotation and accuracy.
When selecting kitting software, logistics professionals should look for several essential features:
- Work in Process (WIP) Inventory Tracking: The system should monitor both the individual parts and the assembled kits, providing insights into current stock, work orders, and partial assemblies. Advanced platforms may also incorporate ABC inventory analysis to prioritize high-value components.
- Kit Forecasting: The software should calculate the number of kits that can be built based on the current stock of components. This requires integration with inventory cycle counting methods and predictive analytics to support demand planning and stock replenishment.
- Min/Max Inventory Tracking: Effective tools will use historical sales data to set minimum and maximum inventory thresholds for both components and finished kits. This ensures optimal inventory turnover, prevents stockouts, and avoids overproduction, which can lead to unnecessary storage costs or backorders.
Conclusion
In summary, kitting transforms complex assembly tasks into a single SKU operation, enabling more accurate forecasting, labor optimization, and better space utilization. Whether used in third-party logistics (3PL) services or internal warehouse operations, kitting supports lean supply chain practices and adds measurable value across the fulfillment process. As logistics networks grow more dynamic, adopting kitting can be a competitive advantage for businesses aiming to scale operations without compromising quality or speed.
Kitting FAQs
What is a kitting lead?
A kitting lead is a key supervisor who coordinates a team of pickers, packers, and shipping personnel to ensure that kits are accurately assembled and prepared for outbound logistics. The kitting lead also oversees the entire workflow of kitting activities, including inventory tracking, workflow organization, process execution, and shipment readiness.
Typically, a kitting lead brings years of hands-on experience in warehouse environments and demonstrates a solid grasp of inventory management principles. Beyond supervising the assembly process, effective kitting leads often identify opportunities to streamline operations by utilizing strategies such as ABC inventory analysis, SKU rationalization, and lean warehousing practices. Their expertise helps optimize picking efficiency, reduce assembly time and minimize order errors.
What are kitting fees?
Kitting fees refer to the additional charges incurred for assembling multiple items into a single, organized shipment before dispatch. Kitting requires extra labor, time, and operational precision, particularly when handling multi-component products, subscription boxes, or customized orders. These fees compensate for the resources needed to sort, group, and package items into a cohesive unit.
Most 3PLs (third-party logistics providers) or fulfillment centers charge kitting fees on an hourly basis, typically ranging between $30 and $50 per hour, depending on the complexity of the kit.
In conclusion, inventory kitting is a powerful strategy that streamlines order fulfillment, reduces warehouse inefficiencies, and enhances customer satisfaction. By bundling related items into a single SKU, businesses can simplify inventory management and improve operational speed. As e-commerce and customer expectations continue to evolve, implementing kitting can give your business a competitive edge and support scalable growth.












 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt 中文 (中国)
中文 (中国)

