In today’s fast-evolving retail landscape, Omnichannel Fulfillment has become a strategic imperative for businesses aiming to deliver consistent customer experiences across every touchpoint. By integrating inventory, orders, and logistics from various channels, companies can meet rising consumer expectations while maintaining operational efficiency. This guide explores why omnichannel fulfillment matters, how it works, and the best tools to implement it effectively. Whether you sell online, in-store, or both, mastering this approach is key to staying ahead.
What Is Omnichannel Fulfillment?
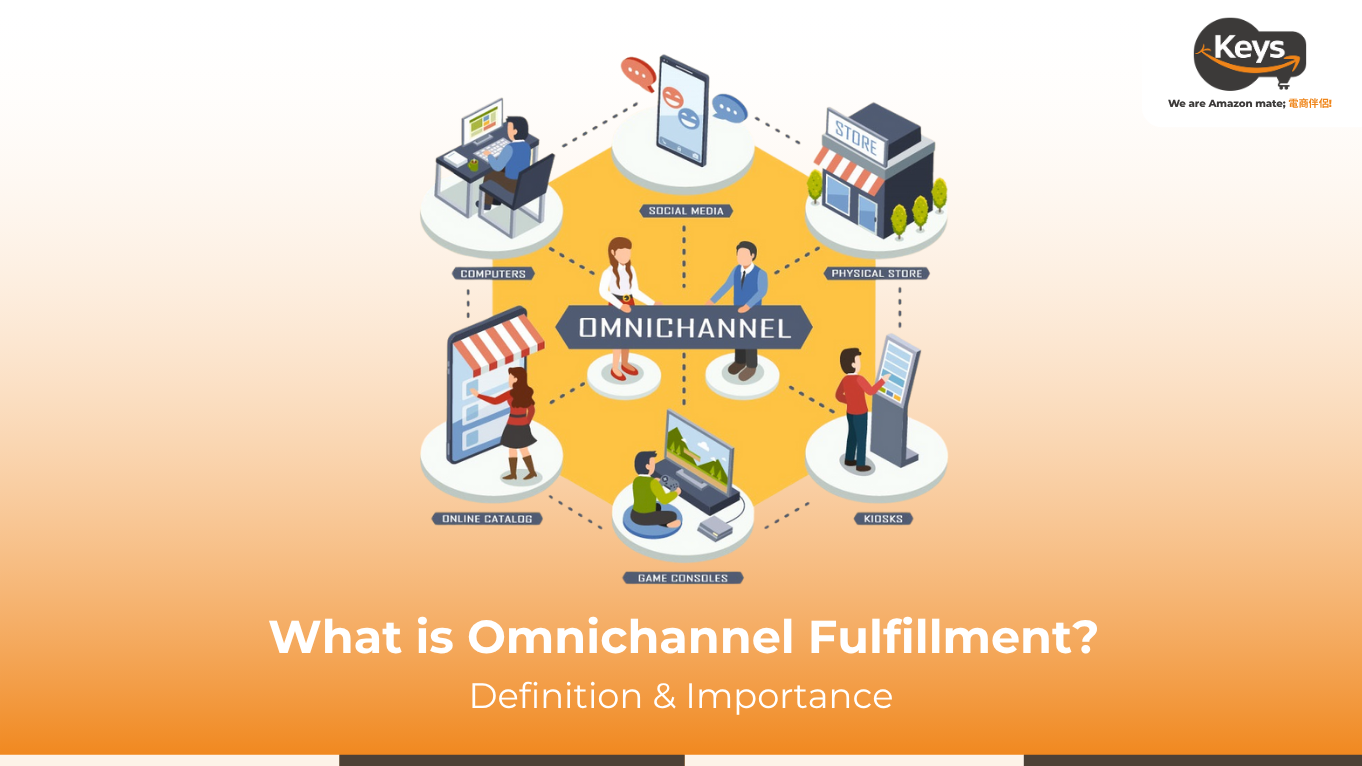
Omnichannel fulfillment is a comprehensive logistics strategy that creates a unified view of inventory and orders across all sales channels, including physical stores, websites, mobile apps, and marketplaces. Unlike multichannel approaches with separate inventory pools, omnichannel breaks down silos to deliver a seamless customer experience across all touchpoints. The strategy relies on advanced technology integration that ensures real-time inventory updates across all channels—when an item sells online, availability instantly adjusts in-store and on other platforms.
Central to this approach is a unified order management system that processes orders from any channel and routes them to optimal fulfillment locations, whether distribution centers, retail stores, or 3PL partners. This customer-centric model enables shoppers to browse, purchase, receive, and return products through any preferred channel combination without friction, creating a cohesive journey regardless of path taken.

Why Omnichannel Fulfillment Matters
The transition towards omnichannel fulfillment is driven by compelling strategic advantages that impact both the customer experience and the bottom line. It addresses the limitations of siloed operations and aligns businesses more closely with the fluid expectations of contemporary consumers.
Reduces Costs Across Multiple Sales Channels
By unifying inventory pools, businesses can significantly improve inventory utilization. Instead of holding separate safety stocks for each channel, a single, shared inventory can serve demand from all sources, reducing overall inventory levels and associated holding costs (storage, insurance, capital).
Furthermore, intelligent order routing, a key component of omnichannel strategies, allows orders to be fulfilled from the location closest to the customer, minimizing shipping distances and transportation costs. Consolidating fulfillment operations and leveraging existing assets like retail stores for fulfillment can also lead to substantial cost savings compared to managing separate logistics networks for each channel.
Enhances Customer Experience Through Seamless Delivery
Consistency is key to customer satisfaction. Omnichannel fulfillment ensures that customers encounter the same product information, pricing, promotions, and brand experience whether they are shopping online, on a mobile app, or in a store. It offers unparalleled flexibility in how customers receive their orders – options like Buy Online, Pick Up In-Store (BOPIS), curbside pickup, ship-from-store, and traditional home delivery cater to diverse preferences for speed and convenience. This seamless integration extends to returns as well, allowing customers to return items purchased online to a physical store, for example. This level of convenience and consistency builds trust and fosters loyalty.

Enables Flexible and Scalable Fulfillment Options
Market demands fluctuate, and sales patterns can shift rapidly between channels. An integrated omnichannel approach provides the agility needed to adapt. Businesses can dynamically allocate inventory and fulfillment capacity based on real-time demand signals. Utilizing retail stores as mini-fulfillment hubs adds significant capacity and flexibility to the network, allowing businesses to scale operations up or down more effectively during peak seasons or promotional events without massive capital investment in new distribution centers. This adaptability is crucial for resilience in a volatile market.
Unlocks New Market Opportunities
Omnichannel strategies effectively blur the lines between online and offline retail, creating synergistic effects. Physical stores become more than just points of sale; they transform into fulfillment centers, return drop-off points, and experiential hubs that drive online traffic (and vice-versa). This integration allows businesses to leverage their entire network footprint to reach more customers and serve existing customers better.
Offering services like BOPIS can drive foot traffic to stores, leading to additional in-store purchases. Conversely, a strong online presence supported by efficient fulfillment can capture sales from geographically dispersed customers who may not have access to a physical store.
Improves Operational Efficiency
Centralizing inventory and order management provides a unified view of operations, leading to significant efficiency gains. Real-time visibility prevents stockouts and overstocking, optimizing inventory turnover. Streamlined order processing reduces manual intervention and errors.
Utilizing stores for fulfillment can improve the productivity of store staff during quieter periods and leverage existing real estate more effectively. Furthermore, the integrated data gathered from all channels provides valuable insights for optimizing everything from warehouse layouts and picking processes to staffing levels and transportation routes, leading to continuous improvement in operational performance.

How Omnichannel Fulfillment Works
Successfully implementing Omnichannel Fulfillment requires a sophisticated orchestration of technology, processes, and data across the entire organization. It’s about creating a connected ecosystem where information flows seamlessly between different touchpoints and operational units.
Integrating Multiple Sales Channels
The foundation is the seamless integration of all platforms where customers interact and purchase. This includes connecting Point-of-Sale (POS) systems in physical stores, ecommerce platforms (like Shopify, Magento, BigCommerce), mobile apps, third-party marketplaces (Amazon, eBay), and social commerce channels.
This integration ensures that product information (descriptions, pricing, images), customer data, and crucially, inventory levels are consistent and synchronized across all channels in real-time or near-real-time. APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) and middleware solutions often play a critical role in enabling communication between these diverse systems.
Real-Time Inventory Visibility
Arguably the most critical element, real-time inventory visibility means having a single, accurate view of all available stock, regardless of its physical location. This requires a centralized inventory management system that receives constant updates from all sales and fulfillment points.
When an item is sold online, picked in a store for BOPIS, or received from a supplier, the central system reflects this change instantly, making the updated quantity available (or unavailable) across all other channels. This prevents overselling and ensures customers see accurate stock information.
Centralized Order Management
Orders originating from any channel flow into a single, centralized Order Management System (OMS). This system acts as the command center, managing the entire order lifecycle from initial capture to final delivery.
The OMS applies predefined business rules (or increasingly, AI-driven logic) to determine the optimal fulfillment location based on factors like inventory availability, customer location, shipping costs, fulfillment node capacity, and specific item requirements. It then routes the order to the appropriate warehouse or store for picking, packing, and shipping.

Diverse Fulfillment Methods (BOPIS, Ship-from-Store, 3PL, etc.)
An omnichannel strategy leverages multiple fulfillment options to enhance speed and convenience. The centralized OMS enables this flexibility by routing orders appropriately:
- BOPIS/click and collect: Orders placed online are routed to a local store for the customer to pick up.
- Ship-from-store (SFS): Online orders are fulfilled using inventory from a nearby retail store, potentially speeding up delivery and utilizing store stock.
- Warehouse fulfillment: Traditional fulfillment from centralized distribution centers.
- 3PL fulfillment: Outsourcing fulfillment to third-party logistics providers, often integrated into the central system.
- Dropshipping: Shipping directly from the supplier/manufacturer to the customer.
Customer-Centric Fulfillment Tracking
Transparency is vital for the customer experience. Once an order is processed and shipped (or ready for pickup), the system should provide customers with real-time tracking information and proactive status updates (e.g., via email or SMS). This visibility extends across the chosen fulfillment method, giving customers confidence and reducing inquiries to customer service (“Where is my order?”).
Data-Driven Decision Making
Integrating data from all channels creates a rich dataset covering customer behavior, sales trends, inventory velocity, fulfillment costs, and operational performance across the entire network. Advanced analytics tools process this data to provide actionable insights.
Businesses can identify best-selling products by channel, understand regional demand patterns, pinpoint bottlenecks in fulfillment processes, measure the profitability of different fulfillment methods, and forecast demand more accurately. This data-driven approach enables continuous optimization of the entire Omnichannel Fulfillment strategy.
Best Omnichannel Fulfillment Software Solutions
Powering a seamless omnichannel operation relies heavily on a well-integrated technology stack. Several categories of software are crucial for managing the complexities involved:
Inventory Management Software
While often a component of larger systems like WMS or ERP, dedicated IMS solutions focus specifically on providing real-time, network-wide inventory visibility. Key features include tracking stock levels across all locations (warehouses, stores, 3PLs), managing SKUs and product variations, supporting cycle counting and physical inventory processes, and providing alerts for low stock or potential discrepancies. Accurate, accessible inventory data is the bedrock of Omnichannel Fulfillment.
Order Management Systems (OMS)
The OMS is the central hub for processing orders from all sales channels. It aggregates orders, provides a unified view of customer order history, manages the order lifecycle, and contains the logic for intelligent order routing – determining the optimal fulfillment source based on configurable rules (proximity, cost, inventory availability, capacity). Advanced OMS platforms offer sophisticated routing capabilities and seamless integration with both sales channels and fulfillment systems.

CRM Platforms for Unified Customer Data
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) platforms consolidate customer data from all interaction points (sales, service, marketing). In an omnichannel context, this provides a 360-degree view of the customer, enabling personalized experiences and consistent service regardless of the channel. Knowing a customer’s purchase history, preferences, and previous interactions allows for targeted marketing, relevant product recommendations, and efficient customer support, enhancing the overall seamless experience.
Analytics and Reporting Tools
To optimize an omnichannel strategy, businesses need to measure performance and derive insights from the vast amounts of data generated. Business Intelligence (BI) and analytics tools integrate data from various systems (OMS, WMS, CRM, ecommerce platforms) to provide dashboards and reports on key metrics. This includes sales performance by channel, inventory turnover rates, fulfillment costs per order, delivery times, customer satisfaction scores, and return rates. These insights are vital for identifying trends, pinpointing inefficiencies, and making informed strategic decisions.
ERP Systems for Cross-Department Integration
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems often serve as the overarching backbone, integrating various business functions including finance, procurement, inventory, order management, and supply chain operations. While specialized systems like OMS and WMS handle specific logistics functions in more detail, the ERP ensures data consistency and process alignment across the entire organization. Integrating the specialized fulfillment software with the central ERP is crucial for seamless financial reconciliation, demand planning, and overall business visibility, ensuring the Omnichannel Fulfillment strategy aligns with broader company objectives.
ERP systems integrate business functions, ensuring data consistency and alignment for effective Omnichannel Fulfillment strategies (Source: Internet)
Incorporating a robust Omnichannel Fulfillment strategy allows businesses to reduce costs, improve service delivery, and adapt seamlessly to customer behavior. With real-time visibility and integrated systems, it turns complex logistics into a competitive edge. As digital commerce expands, choosing the right fulfillment model is no longer a luxury – it’s a necessity. Embrace this transformation to unlock scalable growth and customer satisfaction. Keys Logistics delivers tailored omnichannel fulfillment solutions built to scale with your business. Contact us today to explore how we can optimize your logistics strategy.











 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt 中文 (中国)
中文 (中国)

